Earth and Its Neighbors
Solar Systems: the Sun and the objects that are traveling around it.
Planet: any of the eight large bodies that travel around the Sun and shine by reflecting its light.
Gravity: a force of attraction, or pull, between any object and any other objects around it.
Inertia: the tendency of a moving object to keep moving in a straight line.
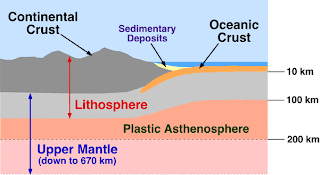
Lithosphere: the hard, outer layer of Earth, about 100 kilometers thick.
Crust: the rocky surface that makes up the top of the lithosphere.
Resource: any material that helps support life on Earth.
Hydrosphere: Earth´s water.
Earth´s Changing Crust
Fault: a crack in the crust, whose sides show evidence of motion.
Geologist: a scientist who studies Earth.
Magma: hot, molten rock deep below Earth´s surface.
Lava: magma that reaches Earth´s surface.
Weathering: the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces.
Erosion: the picking up and carrying away of pieces of rock.
Deposition: the dropping off of bits of eroded rock.
Meteorite: a chunk of rock from space that strikes a surface (such as Earth or the Moon).















No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario